NorOPTIMAL
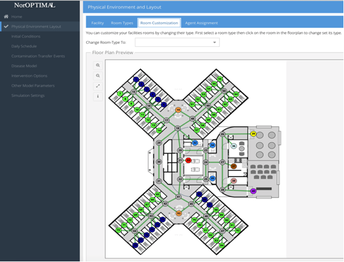
NorOPTIMAL is an agent-based virtual laboratory model where a long term care facility can be designed, risk scenarios with human norovirus contamination and transmission are modeled, and intervention strategies to reduce the spread of norovirus are tested. Data was researched and developed for the probabilities of compliance of residents, health care workers, kitchen and cleaning staff with personal hygiene, likelihood of participating in daily activities, and hand to mouth contact frequency. Data also include transfer rates during tactile contacts, removal of norovirus, disease stage parameters, dose-response, and economic impact. Data for diarrheal and vomiting events are included, such as the shedding rate and contamination of aerosolized particles in vomitus. The daily activity schedule includes the duration, metabolic equivalent, and contact rates between agents and objects for morning care, dining, physical therapy, etc.
NorOPTIMAL is an agent-based virtual laboratory model where a long term care facility can be designed, risk scenarios with human norovirus contamination and transmission are modeled, and intervention strategies to reduce the spread of norovirus are tested. Data was researched and developed for the probabilities of compliance of residents, health care workers, kitchen and cleaning staff with personal hygiene, likelihood of participating in daily activities, and hand to mouth contact frequency. Data also include transfer rates during tactile contacts, removal of norovirus, disease stage parameters, dose-response, and economic impact. Data for diarrheal and vomiting events are included, such as the shedding rate and contamination of aerosolized particles in vomitus. The daily activity schedule includes the duration, metabolic equivalent, and contact rates between agents and objects for morning care, dining, physical therapy, etc.
FDA-iRISK® (Available at FoodRisk.org.)
The FDA-iRISK® model is an interactive, web-based, risk assessment modeling tool that quantitatively compares and ranks public health risks posed by multiple food/hazard combinations (microbial and chemical toxins). The user can test intervention strategies and to compare the baseline and intervention levels of risk, as expressed in a public health metric (disability adjusted life years, or DALYs). Data development for the FDA-iRISK® data library included selecting hazard-commodity pairs from worldwide published risk assessments to ensure representatives from each of the FDA’s 28 RFR commodity categories and microbial and chemical hazards were built in to the model. Data on dose-response, DALY, consumption, and process model scenarios where the behavior of the hazard was modeled for each step a food takes from production, the processing environment to consumption.
The FDA-iRISK® model is an interactive, web-based, risk assessment modeling tool that quantitatively compares and ranks public health risks posed by multiple food/hazard combinations (microbial and chemical toxins). The user can test intervention strategies and to compare the baseline and intervention levels of risk, as expressed in a public health metric (disability adjusted life years, or DALYs). Data development for the FDA-iRISK® data library included selecting hazard-commodity pairs from worldwide published risk assessments to ensure representatives from each of the FDA’s 28 RFR commodity categories and microbial and chemical hazards were built in to the model. Data on dose-response, DALY, consumption, and process model scenarios where the behavior of the hazard was modeled for each step a food takes from production, the processing environment to consumption.
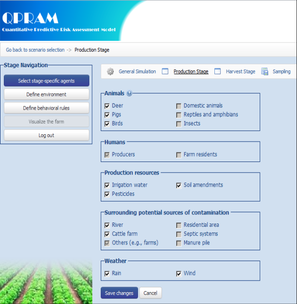
QPRAM
The Quantitative Predictive Risk Assessment Model (QPRAM) is an agent-based, virtual laboratory that models production and processing practices and risk factors from farm to fork for E. coli O157:H7 and leafy greens, and Salmonella and tomatoes. QPRAM is designed to characterize baseline risks and estimate potential reductions in risk that may be achieved through proposed interventions to prevent, reduce, or eliminate pathogen contamination at critical points along the farm-to-fork continuum. Data development included quantitative estimates for the production, harvest, and processing stages of the farm to fork quantitative probabilistic risk assessment model for E. coli O157:H7 and Romaine lettuce and Salmonella spp. and tomatoes. Model estimates required data on wild animals, domestic animals farms, hazards, irrigation water, humans, pesticides, rivers, soil amendments, environmental phenomena, food processing steps, pathogen behavior during processing steps, and inactivation technologies.
The Quantitative Predictive Risk Assessment Model (QPRAM) is an agent-based, virtual laboratory that models production and processing practices and risk factors from farm to fork for E. coli O157:H7 and leafy greens, and Salmonella and tomatoes. QPRAM is designed to characterize baseline risks and estimate potential reductions in risk that may be achieved through proposed interventions to prevent, reduce, or eliminate pathogen contamination at critical points along the farm-to-fork continuum. Data development included quantitative estimates for the production, harvest, and processing stages of the farm to fork quantitative probabilistic risk assessment model for E. coli O157:H7 and Romaine lettuce and Salmonella spp. and tomatoes. Model estimates required data on wild animals, domestic animals farms, hazards, irrigation water, humans, pesticides, rivers, soil amendments, environmental phenomena, food processing steps, pathogen behavior during processing steps, and inactivation technologies.
|
FDA Fresh Produce Risk Ranking Tool (available at FoodRisk.org)
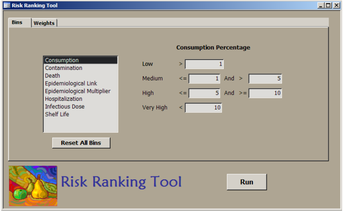
P3ARRT (Pathogen-Produce Pair Attribution Risk Ranking Tool, now named FDA Fresh Produce Risk Ranking Tool) is a semi-quantitative risk ranking tool built to prioritize pathogen and fresh produce commodity pairs for risk assessment based on epidemiological, health, and commodity-based criteria. Outbreak data was used to identify 51 pathogen-commodity pairs, and data was compiled for each pair for the following criteria: Epidemiological link, Disease multiplier, Hospitalization rate, Death rate, Population susceptibility, Infectious dose, Prevalence of contamination, Growth potential/shelf life, and Consumption. The risk ranking tool provides a data-driven method to prioritize pathogen-produce commodities for further quantitative microbial risk assessment effort. |